Heart Medication Interaction Checker
Check for dangerous combinations
Enter medications to see if they create dangerous interactions. This tool checks against known high-risk heart medication combinations.
Interaction Found
Estimated risk increase:
Heart medications are drugs prescribed to treat conditions like hypertension, arrhythmia, heart failure, and coronary disease. When they meet the wrong partner, the result can be a life‑threatening dangerous drug combinations that boost the chance of heart attack, stroke, or sudden death. These medicines include anticoagulants, beta‑blockers, ACE inhibitors, statins, and many others that millions of patients rely on daily. Understanding why these interactions happen and how to spot them is the first step to staying safe.
Why drug interactions matter for heart health
Older adults are the most vulnerable. The National Center for Health Statistics reports that 57 % of women and 44 % of men aged 65+ take five or more prescription drugs each week. Each extra pill adds a new chance for a clash.
A 2023 study in Pharmacoepidemiology & Drug Safety found that taking two or more drugs with known cardiovascular side effects doubled the risk of a heart attack, and three such drugs pushed the risk up by more than 200 %. In plain language: the more risky meds you stack, the steeper the danger curve climbs.
Beyond the numbers, the human cost is stark. The FDA estimates about 106,000 deaths a year in the United States stem from adverse drug reactions, making them the fourth leading cause of death.
The most hazardous heart medication combos
Not every mix is equally risky. Here are the pairings that consistently show the biggest spikes in harm:
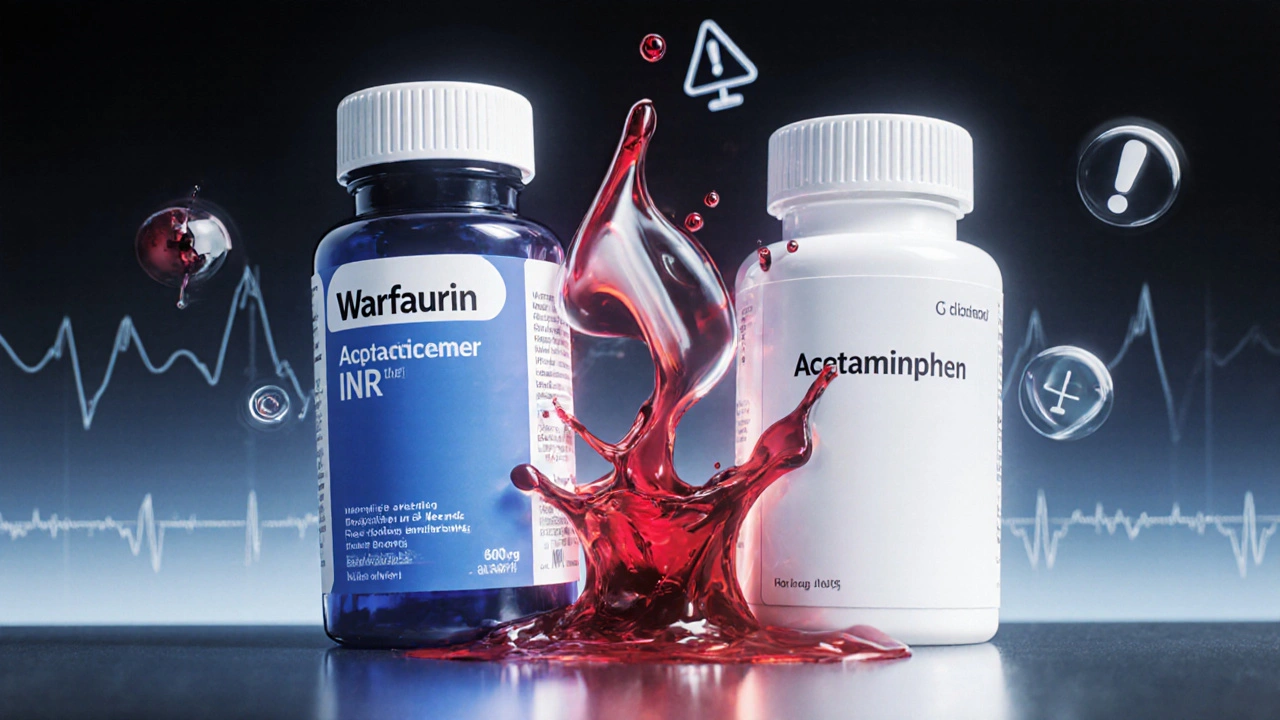
- Warfarin + Acetaminophen: Chronic acetaminophen can lift INR by 2‑3 points, turning a stable anticoagulation into a bleeding emergency.
- Warfarin + Ibuprofen (or other NSAIDs): Increases gastrointestinal bleeding risk by roughly 300 % compared with warfarin alone.
- PDE‑5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis) + Nitrates: Triggers life‑threatening hypotension, sometimes dropping systolic pressure below 70 mmHg.
- Statins + Amiodarone: Raises the chance of muscle toxicity (myopathy) by 400‑500 %.
- ACE inhibitors + Potassium supplements: Can push serum potassium over 5.5 mEq/L in nearly 19 % of patients, risking dangerous heart rhythms.
- Digoxin + Verapamil: Raises digoxin serum levels by 60‑75 %, setting the stage for digoxin toxicity.
- Opioids + Benzodiazepines: Overdose risk jumps 300‑500 % and adds a hidden cardiovascular strain.
These combos are not just theoretical; they appear in emergency rooms daily.
How the risk spikes: what the numbers say
| Combination | Main Risk | Approx. Risk Increase |
|---|---|---|
| Warfarin + Acetaminophen | Bleeding (INR rise) | +200 % |
| Warfarin + Ibuprofen | GI bleeding | +300 % |
| PDE‑5 inhibitor + Nitrate | Severe hypotension | +400 % |
| Statin + Amiodarone | Myopathy | +450 % |
| ACE‑I + Potassium supplement | Hyperkalemia | +250 % |
| Digoxin + Verapamil | Digoxin toxicity | +70 % |
| Opioid + Benzodiazepine | Respiratory & cardiovascular collapse | +400 % |
These percentages come from a mix of CDC data, MedicineNet analyses, and peer‑reviewed clinical studies. They illustrate that a single extra pill can multiply danger by several hundred percent.
Practical steps to keep your meds safe
Knowing the bad pairs is only half the battle. Here’s what patients and caregivers can do every day:
- Keep a master list: Write every prescription, over‑the‑counter drug, and supplement with exact dose (e.g., “lisinopril 10 mg once daily”). Update it within the past 30 days and bring it to every appointment.
- Use a single pharmacy: When all prescriptions funnel through one pharmacy, the pharmacist can run a comprehensive interaction check.
- Ask before you add anything: Even “harmless” OTC meds like ibuprofen or acetaminophen need a quick safety check with your doctor.
- Schedule medication therapy management (MTM) sessions: A 20‑30 minute review covered by Medicare Part D can catch hidden risks.
- Leverage technology: Many electronic health records now flag dangerous combos with 85‑92 % accuracy. Enable alerts on your phone apps (e.g., Medisafe, MyChart).
Following these habits can cut adverse drug events by roughly 30 %, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
Tools and resources for checking interactions
Several free or insurance‑covered resources make checking easier:
- FDA’s Drug Interaction Database: Search any two drugs and see if the agency has issued a warning.
- Beers Criteria (2023 update): Lists 30 high‑risk combos for adults over 65, including many heart meds.
- Pharmacy‑run Clinical Decision Support: If your pharmacy uses a system like FirstDataBank, you’ll automatically get alerts.
- Patient‑focused apps: Medisafe, MyMediCheck, and CareZone allow you to input every medication and get a real‑time interaction report.
Remember: technology helps, but a conversation with your prescriber is still the gold standard.

Quick checklist of combos to avoid
- Warfarin with any NSAID (ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac)
- Warfarin with regular acetaminophen use (>2 g/day)
- PDE‑5 inhibitor with any nitrate (e.g., nitroglycerin, isosorbide)
- Statin with amiodarone or other CYP3A4 inhibitors
- ACE inhibitor with potassium chloride or high‑potassium foods in supplement form
- Digoxin with verapamil, diltiazem, or quinidine
- Opioid with benzodiazepine or alcohol
Cross‑checking each item on this list before a new prescription can save you from a serious event.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can over‑the‑counter pain relievers be safe with my heart meds?
Most OTC NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac) can increase bleeding risk when taken with anticoagulants like warfarin or clopidogrel, and they may blunt the effect of blood‑pressure drugs. Acetaminophen is usually safer, but high daily doses can still raise INR. Always check with your pharmacist before using any OTC pain pill.
Are dietary supplements such as St. John’s wort dangerous?
Yes. St. John’s wort induces liver enzymes that speed up the breakdown of many heart drugs, especially warfarin and certain statins, potentially lowering their effectiveness and leading to clotting or cholesterol spikes.
What should I do if I’m already on a risky combination?
Contact your prescriber immediately. Often the dose can be adjusted, the drug swapped for a safer alternative, or a monitoring plan (e.g., frequent INR checks) can be set up. Do not stop any medication without professional guidance.
Do fixed‑dose combination pills reduce interaction risk?
Fixed‑dose combos, like the recent dapagliflozin‑sacubitril‑valsartan pill, bundle drugs that are already proven to work well together, cutting the chance of unpredictable interactions. Studies show a 15‑22 % drop in adverse events compared with taking each component separately.
How often should I have my medication list reviewed?
At every major change-new prescription, dose adjustment, or addition of an OTC product. Even if nothing seems new, an annual comprehensive review is a good safety habit.
Staying alert, keeping records, and using professional checks are the best defense against deadly drug combos. Your heart depends on it.


13 Comments
October 26, 2025 Diana Jones
Honestly, folks, navigating cardiac pharmacotherapy is like conducting a high‑stakes orchestra-each molecule must hit its cue or the whole performance collapses. Your list of perilous pairings reads like a cheat sheet for adverse event detectives, and that’s exactly the vibe we need to champion. Keep that master medication ledger updated; think of it as a living protocol that preempts hypercoagulable crescendos and hypotensive fades. Remember, the sooner you flag a warfarin‑NSAID duet, the less likely you’ll have to scramble for a blood‑product en‑suite.
Stay vigilant and keep the rhythm clean.
October 29, 2025 Carolyn Cameron
While the preceding admonition admirably underscores the necessity of meticulous record‑keeping, it would be remiss not to invoke the tenets of evidence‑based medicine in this discourse. The cited statistics, albeit compelling, ought to be juxtaposed with randomized controlled trials that delineate causality rather than correlation. Moreover, the discourse could benefit from a stratified analysis by comorbidities, thereby affording clinicians a granular risk matrix. In sum, a more scholarly exposition would elevate this treatise to the requisite academic rigor.
October 31, 2025 sarah basarya
Seriously? You’ve just listed the “dangerous combos” like it’s a trendy playlist for the frail. People actually trust these meds, and you’re serving them a billboard of doom without any nuance about dosage thresholds or patient‑specific metabolism. It’s all hype until someone actually stops a pill and feels the panic spike. I can’t believe we’re still parading the same oversimplified warnings as if the average reader has a PhD in pharmacokinetics.
November 2, 2025 Samantha Taylor
Allow me to interject with a modicum of precision: the interaction magnitude between warfarin and acetaminophen is dose‑dependent, typically manifesting when daily intake exceeds 2 g, as delineated in the FDA’s pharmacovigilance report of 2022. Furthermore, the cytochrome P450 inhibition profile of amiodarone amplifies statin serum concentrations, thereby necessitating a 50 % dose reduction to mitigate myopathic risk. In the realm of nitrates paired with PDE‑5 inhibitors, the resulting venodilatory cascade can precipitate a precipitous systolic drop below 70 mmHg, a phenomenon well‑documented in the Circulation journal. Hence, a blanket admonition without contextual dosage parameters is, frankly, intellectually negligent.
November 5, 2025 Ben Dover
From an analytical standpoint, the prevalence data cited merits a deeper statistical interrogation. The 57 % polypharmacy rate among women over 65, while alarming, conflates appropriate guideline‑driven therapy with inadvertent polypharmacy. A multivariate regression model accounting for comorbid burden would elucidate the true independent effect of drug‑drug interactions on mortality. Moreover, the interaction scoring system employed appears to be derived from heterogeneous sources, potentially inflating risk estimates. A rigorous meta‑analysis would be requisite to substantiate these assertions.
November 7, 2025 Katherine Brown
I appreciate the methodological rigor you propose, yet we must also acknowledge the pragmatic constraints faced by primary‑care practitioners. While sophisticated regression models offer theoretical clarity, the day‑to‑day workflow often precludes such depth of analysis. A balanced approach that integrates both evidence‑based risk stratification tools and clinician intuition may bridge the gap between statistical purity and real‑world applicability. In fostering collaborative discourse, we can advance patient safety without alienating frontline providers.
November 9, 2025 Ben Durham
Look, the safest route is to keep everything in one pharmacy’s system so the software can shout out any red flags before you even pick up the pill bottle. It’s like having a co‑pilot that constantly scans the horizon for turbulence. Make sure you update that list every few weeks-don’t let it become a relic from last year’s appointment. When you do, you’ll catch those sneaky NSAID‑warfarin combos before they turn a routine check‑up into an emergency room sprint.
November 11, 2025 Tony Stolfa
Stop ignoring the warnings and just keep taking the meds like a hero.
November 14, 2025 Joy Dua
Within the labyrinth of pharmacologic interplay lies a paradoxical dance where molecules whisper promises of salvation while secretly plotting discordant crescendos it is a reminder that the human body is a fragile tapestry woven from chemistry and will
November 16, 2025 Holly Kress
That’s a poetic way to frame the issue, and it underscores why open communication with your prescriber is essential. By treating the medication list as a living document, you empower yourself to spot those “whispers” before they become dangerous shouts. Encourage your healthcare team to review the list regularly, and don’t shy away from asking about any over‑the‑counter products you might be taking. A collaborative approach turns that fragile tapestry into a more resilient weave.
November 18, 2025 Chris L
Exactly-teamwork makes the dream work. When patients, pharmacists, and doctors sync up, the chances of missing a risky combo drop dramatically. I’ve seen clinics that schedule quarterly medication reviews and they cut adverse events by a solid third. So keep that dialogue alive, and watch your heart health improve step by step.
November 21, 2025 Charlene Gabriel
First and foremost, let me commend everyone who has taken the time to read through this extensive overview of cardiac drug interactions; such diligence is the cornerstone of proactive health management. The sheer volume of medications that a typical older adult may be prescribed can feel overwhelming, but breaking the information down into manageable chunks makes the task far less daunting. One effective strategy is to categorize your medicines by therapeutic class-anticoagulants, antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics, lipid‑lowering agents, and so forth-so you can more easily spot potential culprits within each group. Next, create a master medication list that includes not only prescription drugs but also over‑the‑counter products, herbal supplements, and any “as‑needed” medications, noting the exact dosage and timing for each. This list should be reviewed at every healthcare encounter, and you should feel empowered to request a medication reconciliation whenever a new drug is added.
In addition to personal record‑keeping, leverage technology-most pharmacy apps now offer real‑time interaction alerts that flag dangerous pairings an instant after you input a new entry. However, never rely solely on software; the nuances of individual metabolism, renal function, and genetic polymorphisms often escape algorithmic detection, necessitating a clinician’s judgment. Discuss with your pharmacist about the possibility of using a single pharmacy for all prescriptions, which enables a comprehensive interaction check that might otherwise slip through the cracks. If you ever notice symptoms such as unexpected bruising, muscle weakness, dizziness, or palpitations, consider these as potential red flags that warrant immediate medical evaluation.
Furthermore, consider enrolling in medication therapy management (MTM) programs, especially if you are on Medicare Part D, as these sessions provide a structured review that can uncover hidden hazards. For those caring for a loved one, maintain an up‑to‑date binder or digital file that can be accessed quickly in an emergency, and share this information with all members of the care team. Remember that lifestyle factors-dietary potassium intake, alcohol consumption, and even certain foods-can interact with medications like ACE inhibitors or potassium supplements, amplifying cardiac risk. By adopting a holistic view that integrates medication vigilance with lifestyle moderation, you create a robust defense against adverse drug events.
Finally, don’t underestimate the power of patient education; the more you understand the why behind each warning, the more likely you are to adhere to safe practices. Continue to ask questions, stay informed through reputable sources, and maintain an open line of communication with your healthcare providers. In doing so, you not only protect your heart but also set an empowering example for others navigating the complex world of medication management.
November 23, 2025 Leah Ackerson
Wow, that's a marathon of advice-thanks for the literary workout! 📚 While I love the thoroughness, sometimes less is more; a quick “check your meds monthly” can be just as effective for many. Still, your passion shines through, and those emojis definitely lighten the mood. 🌟 Keep spreading the knowledge, but remember to keep it bite‑size for the restless reader.
Write a comment